Introduction to Asymptotes
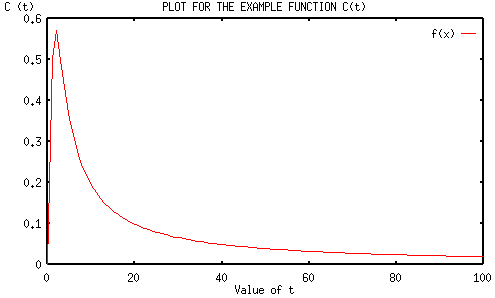
The graph can be easily interpreted if the bounds of the graph are known. The limits which bound the function are called asymptotes. The graph of the example function C(t) is again drawn for convenience.
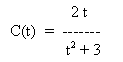
Thus, an asymptote can be defined as a line that is the limiting position of a tangent to a curve as its point of contact recedes indefinitely along an infinite branch of the curve.
![]()
Types of Asymptotes
There are three types of asymptotes. They are horizontal asymptotes, vertical asymptotes and oblique asymptotes. Horizontal asymptotes are lines of the form y = L , where L is a constant.
Horizontal asymptotes are lines of the form y = L , where L is a constant.
 Vertical asymptotes are lines of the form x = L , where L is a constant.
Vertical asymptotes are lines of the form x = L , where L is a constant.
 Oblique asymptotes are lines of the form y = mx + b where m is the slope of the line and b is a constant.
Oblique asymptotes are lines of the form y = mx + b where m is the slope of the line and b is a constant.